Here's a link to a nice pdf of
sheep brain dissections.
Meninges (Dura mater, Arachnoid mater, Pia mater) - no sheep pictures (not visible); identification on human brain for lab exam 2 of Dura Mater & Arachnoid mater.
Falx cerebri (of Dura mater):
 |
| Falx cerebri is not directly pictured: it is the vertical "shelf" of Dura Mater (outermost/superficial layer of the 3 meninges) between the 2 Cerebral Hemispheres (i.e. forms the lining of the Longitudinal Fissure). |
Tentorium cerebelli (of Dura mater):
 |
| Tentorium cerebelli is the "strip" of Dura Mater between the Cerebrum and Cerebellum; more specifically, Tentorium cerebelli lines the Transverse fissure. |
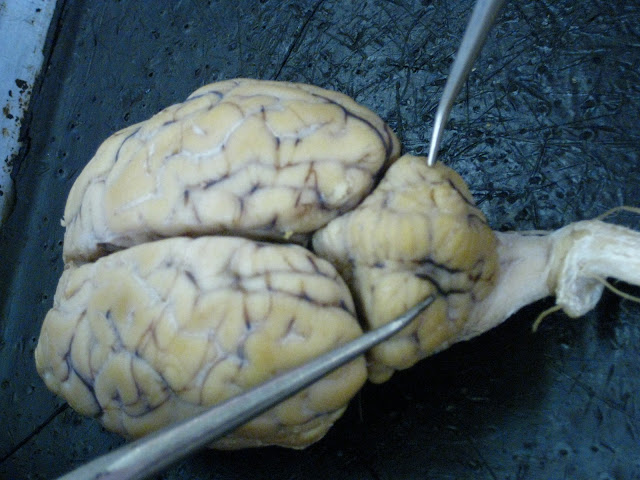
Cerebral Hemispheres (2) - aka Cerebrum/Telencephalon:
Longitudinal fissure (of Telencephalon/Cerebrum):
 |
| pic 1 |
 |
| pic 2 |
Gyrus:
 |
| Gyri are "hills" of brain tissue. |
Sulcus:
 |
| Sulci are "valleys" in brain tissue. |
Corpus callosum:
 |
| Internal view 1 of Corpus callosum ("roof" of the lateral ventricles, aka 1st and 2nd ventricles). |
 |
| External view 1 of Corpus callosum. |
 |
| Internal view 2 of Corpus Callosum. |
 |
| External view 2 of Corpus callosum. |
Gray matter (non-myelinated axons):
 |
| Gray matter of Cerebellum/arbor vitae. |
White matter (myelinated axons, Oligodendrocytes):
 |
| White matter of Cerebellum/arbor vitae. |
Frontal lobe (of Telencephalon/Cerebrum):
Olfactory bulbs (of Frontal lobe):
 |
| Probe is pointing to the left Olfactory bulb (brain is shown from an anterior view, held upside down); Olfactory bulb is the bulb-like expansion of the Olfactory tract on the inferior surface of the Frontal Lobe portion of each cerebral hemisphere. |
Olfactory tract (of Frontal lobe):
 |
| Probe is pointing to the left Olfactory tract (anterior view of brain, held upside down); Olfactory tract is a bundle of axons located on the inferior surface of the Frontal lobe portion of each cerebral hemisphere. |
Parietal lobes (of Telencephalon/Cerebrum):
Temporal lobes (of Telencephalon/Cerebrum):
 |
| Probe is pointing to the left Temporal lobe. |
Occipital lobes (of Telencephalon/Cerebrum):
Diencephalon:
 |
| Diencephalon includes the following areas/structures: 3rd ventricle, Thalamus (wall of 3rd ventricle), Hypothalamus (floor of 3rd ventricle), Optic chiasm(a), Tuber cinereum, Infundibulum (stalk of pituitary gland), Pituitary gland, and Mammillary body. |
Optic chiasm(a):
 |
| Optic chiasma (fully "X" shaped, normally) has been cut; Optic chiasma is where the optic nerves partially decussate (cross). The Optic chiasma is located at the bottom of the brain, immediately inferior to (below) the Hypothalamus. |
 |
| Sagittal section/view of Optic chiasma. |
Pituitary gland: (cut off in all specimens, no class picture available for sheep brain).
Infundibulum (aka "Pituitary stalk" of Pituitary gland):
 |
| Probe is pointing through the hole where the Infundibulum would normally emerge, had it not been cut off. Infundibulum is the "stalk"/small tube that the Pituitary gland hangs from. |
Tuber cinereum (of Pituitary gland):
 |
| Tuber cinereum is the tan-colored circle surrounding the hole where the Infundibulum would normally be. |
Mammillary body:
 |
| Mammillary body is the structure located opposite the Optic chiasma. Function of Mammillary body has to do with linking emotion with olfactory (sense of smell) memory. |
Cerebellum (Latin for "little brain", part of Metencephalon):
 |
| Sagittal section/view of Cerebellum. |
 |
| Bird's Eye view of Cerebellum. |
 |
| Side view of Cerebellum. |
Transverse fissure (of Cerebellum):
 |
| Transverse Fissure of the Cerebellum is where the Tentorium cerebelli (made of the Dura mater meninx) would normally be located. |
Cerebellar hemispheres (of Cerebellum):
Arbor vitae (of Cerebellum):
 |
| Sagittal section of Cerebellum reveals Arbor vitae ("Tree of Life" pattern of white matter). |
Midbrain
(aka "Mesencephalon")- structures of the Midbrain are: Pineal gland,
Corpora quadrigemina, Cerebral aqueduct, Cerebral peduncles.
Cerebral peduncles (part of Midbrain or Mesencephalon; of Brainstem):
 |
| Probes are pointing to the left and right Cerebral peduncles, respectively, on the inferior surface of the brain. |
 |
| Lateral/side view of a Cerebral peduncle. |
Corpora quadrigemina (aka "tectum"; of Brainstem):
 |
| Probe is pointing to the Superior colliculi, but this is the general area of the Corpora quadrigemina of the Brainstem, tucked between the Cerebrum and Cerebellum. |
Superior colliculi (of Corpora quadrigemina; of Brainstem):
 |
| Probe is pointing to the Right Superior colliculus (bigger "butt cheek"). |
Inferior colliculi (of Corpora quadrigemina; of Brainstem:
 |
| Probe is pointing to the Right Inferior colliculus (smaller "butt cheek") of the Corpora quadrigemina, which is part of the Brainstem; In general, the Brainstem consists of the following structures/areas: Midbrain (Mesencephalon), Pons (Myelencephalong), and Medulla oblongata (also Myelencephalon). |
 |
| Another view of the Inferior colliculi of Corpora quadrigemina. |
|
Pineal gland (of Brainstem):
 |
| Posterior view of Pineal gland. |
 |
| Sagittal section/view of Pineal gland. |
Pons (part of Myelencephalon; of Brainstem):
 |
| Pons is located immediately posterior to the Cerebral penduncles. |
Medulla oblongata (part of Myelencephalon; of Brainstem):
 |
| Probe indicates general area of Medulla oblongata. |
 |
| Sagittal section/view of Medulla oblongata. |
Ventral median fissure (of Medulla oblongata):
 |
| Probe is pointing to the Ventral median fissure (dark line) of the Medulla oblongata. |